Blog Articles
Discover our latest articles, guides and tips

Retirement Savings Strategies Using Retirement Calculators
Retirement savings strategies are no longer optional. Planning for retirement has become a necessity in a world of risin...

Currency Conversion Mistakes Travelers Always
Currency conversion mistakes are one of the most common and costly problems travelers face when visiting another country...

How to Track and Reduce Your Carbon Footprint with a Carbon Footprint Calculator
Carbon footprint calculator tools have become essential for anyone who wants to understand and reduce their environmenta...

Is It Better to Rent or Buy in 2026
Is it better to rent or buy in 2026 is one of the most common financial questions people are asking today. Rising intere...

How to Use a Loan Repayment Calculator to Pay Off Debt Faster
Using a loan repayment calculator is one of the most effective ways to take control of your debt and shorten the time it...
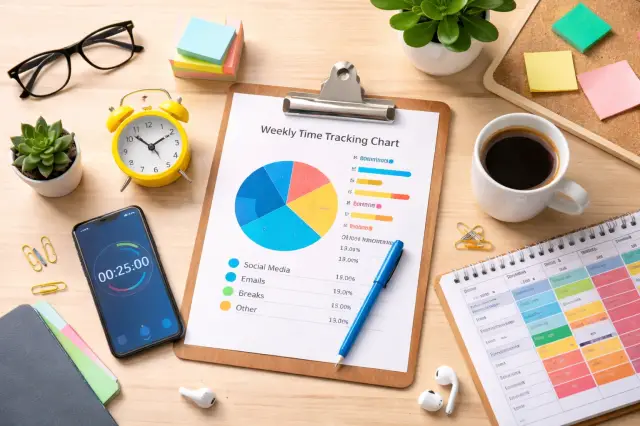

How Much Time Do You Waste Every Week A Real Productivity Breakdown
Time is one of the few resources you cannot recover. Yet most people underestimate how much of it they waste every singl...

How many calories do you really need per day
How many calories you really need per day is one of the most common and misunderstood health questions. The answer is no...

How to Calculate Academic Grades and GPA Easily
Calculating academic grades and GPA is one of the most common challenges for students at all education levels. From high...

Are You Really Productive or Just Busy
The question of whether you are truly productive or simply busy has become more relevant than ever. Modern work culture ...
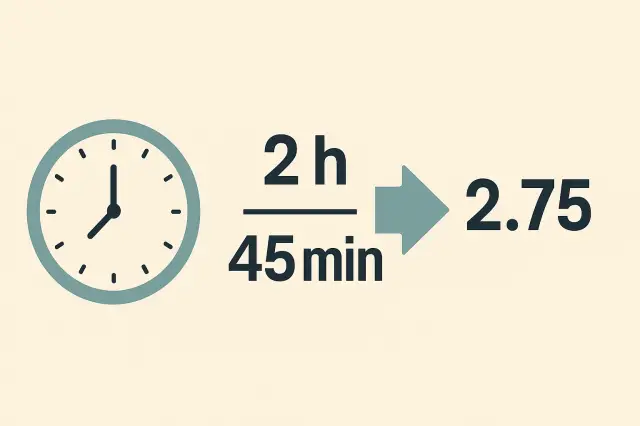
Hours and Minutes to Decimal Converter How to Calculate Work Time Accurately
The hours and minutes to decimal converter is an essential tool for anyone who needs to calculate work time accurately. ...

The Hidden Math Behind Everyday Decisions How Percentage Calculation Shapes Your Life
Percentage calculation plays a fundamental role in daily life, even when we are not consciously thinking about it. From ...

How To Plan a Countdown for Goals Using Digital Tools
A countdown timer is one of the most effective digital tools for staying focused on goals, deadlines, and long-term obje...
